Introduction
TVM is an open deep learning compiler stack to compile various deep learning models from different frameworks to CPU, GPU or specialized accelerators. TVM supports model compilation from a wide range of front ends like Tensorflow, Onnx, Keras, Mxnet, Darknet, CoreML and Caffe2. TVM compiled modules can be deployed on backends like LLVM (Javascript or WASM, AMD GPU, ARM or X86), NVidia GPU (CUDA), OpenCL and Metal.
TVM supports runtime bindings for programming languages like Javascript, Java, Python, C++… and now Golang. With a wide range of frontend, backend and runtime bindings, TVM enables developers to integrate and deploy deep learning models from a variety of frameworks to a choice of hardware via many programming languages.
The TVM import and compilation process generates a graph JSON, a module and a params. Any application that integrates the TVM runtime can load these compiled modules and perform inference. A detailed tutorial of module import and compilation using TVM can be found at tutorials.
TVM now supports deploying compiled modules through Golang. Golang applications can make use of this
to deploy the deep learning models through TVM. The scope of this blog is the introduction of gotvm package,
the package build process and a sample application using gotvm to load a compiled module and perform inference.
Package
The golang package gotvm is built on top of TVM’s C runtime interface. The API in this package
abstracts the native C types and provides Golang compatible types. The package source can be found
at gotvm.
This package leverages golang’s interface, slices, function closures and implicitly handles the necessary conversions across API calls.
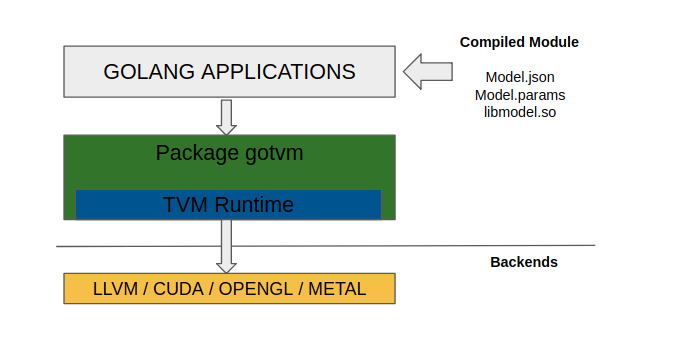
How to
As shown in the below diagram gotvm enables golang applications to integrate deep learning models
from various frameworks without the hassle of understanding each framework related interface API.
Developers can make use of TVM to import and compile deep learning models and generate TVM artifacts.
gotvm package provides golang friendly API to load, configure, feed input and get output.
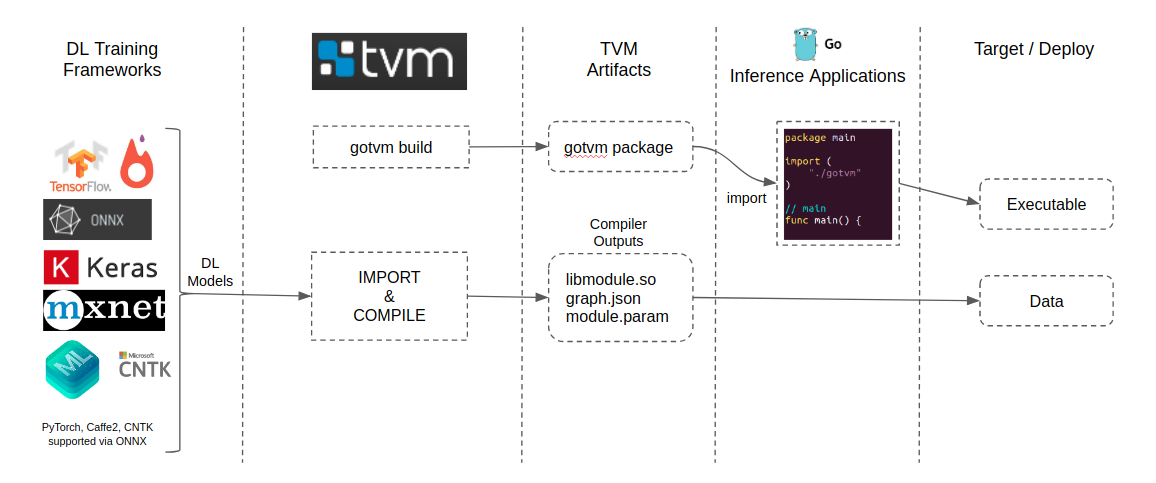
TVM Compile Deep Learning Models tutorials are available to compile models from all frameworks supported by the TVM frontend. This compilation process generates the artifacts required to integrate and deploy the model on a target.
API
gotvm package provides a handful of datatypes and API functions to initialize, load and infer
from a golang application. Like any other golang package we just need to import gotvm package here.
- Module : The Module API can be used to load a TVM compiled module into TVM runtime and access any functions.
- Value : The Value API provides helper functions to set arguments or get return values in golang types like basic types or slices.
- Function : The Function API is useful for getting handles to functions and invoking them.
- Array : The Array API is useful for setting and getting Tensor data via golang slice.
- Context : The Context API contains helper functions to build backend context handles.
Example
A simple example with inline documentation of loading a compiled module and performing inference is shown below. For simplicity the error handling is ignored here, but is important in real applications.
package main
// Import compiled gotvm package.
import (
"./gotvm"
)
// Some constants for TVM compiled model paths.
// modLib : Is the compiled library exported out of compilation.
// modJson : TVM graph JSON.
// modParams : Exported params out of TVM compilation process.
const (
modLib = "./libdeploy.so"
modJSON = "./deploy.json"
modParams = "./deploy.params"
)
// main
func main() {
// Some util API to query underlying TVM and DLPack version information.
fmt.Printf("TVM Version : v%v\n", gotvm.TVMVersion)
fmt.Printf("DLPACK Version: v%v\n\n", gotvm.DLPackVersion)
// Import tvm module (so).
modp, _ := gotvm.LoadModuleFromFile(modLib)
// Load module on tvm runtime - call tvm.graph_runtime.create
// with module and graph JSON.
bytes, _ := ioutil.ReadFile(modJSON)
jsonStr := string(bytes)
funp, _ := gotvm.GetGlobalFunction("tvm.graph_runtime.create")
graphrt, _ := funp.Invoke(jsonStr, modp, (int64)(gotvm.KDLCPU), (int64)(0))
graphmod := graphrt.AsModule()
// Allocate input & output arrays and fill some data for input.
tshapeIn := []int64{1, 224, 224, 3}
tshapeOut := []int64{1, 1001}
inX, _ := gotvm.Empty(tshapeIn, "float32", gotvm.CPU(0))
out, _ := gotvm.Empty(tshapeOut)
inSlice := make([]float32, (244 * 244 * 3))
rand.Seed(10)
rand.Shuffle(len(inSlice), func(i, j int) {inSlice[i],
inSlice[j] = rand.Float32(),
rand.Float32() })
inX.CopyFrom(inSlice)
// Load params
bytes, _ = ioutil.ReadFile(modParams)
funp, _ = graphmod.GetFunction("load_params")
funp.Invoke(bytes)
// Set module input
funp, _ = graphmod.GetFunction("set_input")
funp.Invoke("input", inX)
// Run or Execute the graph
funp, _ = graphmod.GetFunction("run")
funp.Invoke()
// Get output from runtime.
funp, _ = graphmod.GetFunction("get_output")
funp.Invoke(int64(0), out)
// Access output tensor data.
outIntf, _ := out.AsSlice()
outSlice := outIntf.([]float32)
// outSlice here holds flattened output data as a golang slice.
}
gotvm extends the TVM packed function system to support golang function closures as packed functions.
Examples available to register golang
closure as TVM packed function and invoke the same across programming language barriers.
Show me the code
References
- [1] Go Programming Lang
- [2] Go Documentation Guide Lines
- [3] Go Testcase Framework
- [4] Go CFFI
- [5] Go Variadic Functions
- [6] CFFI Ref
- [7] Go Finalizers
